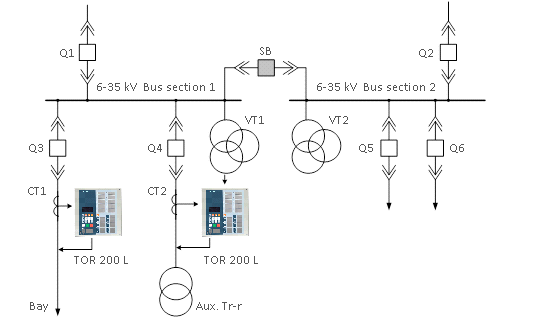
TOR 200 L devices are intended for relay protection and automatic control of MV overhead and/or cable lines, lines towards step-down transformers. They are also suitable for protection of lines supplying small motors and lines to capacitor banks without differential protection.
Main functions
- PTOC/PIOC (50/51) - three-stage time delayed overcurrent protection
- PDEF/PSDE (67N) two-stage time delayed directional earth fault overcurrent protection
- PPBR (46) - broken live conductor protection (unbalance protection)
- PVOC (51V) – voltage controlled overcurrent protection
- PTUV (27) - undervoltage protection
- PTOV (59) - residual voltage protection
- RBRF (50BF) - breaker failure protection
- RREC (79) – automatic reclosing
- PFRQ (PTUF, PFRC) - frequency load shedding
- CSWI - local and remote breaker control
- SCBR - circuit breaker status monitoring (control circuit, SF6 pressure, tripping time, etc.)
- RDRE - disturbance and event recording
- RFLO - fault location
- MMXU – measurements of current, voltage, frequency etc.
- local, warning and alarm signaling
- arc protection by sensor signal detection
- acceleration of current protection
- circuit breaker mechanical and switching life-time monitoring
Functionality of the IED can be changed according to certain technical requirements of customers.
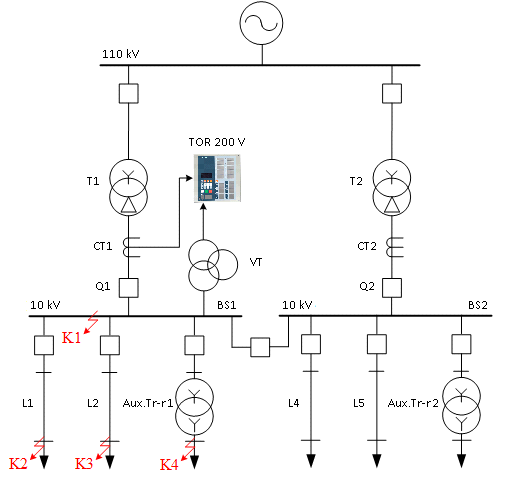
TOR 200 V devices are intended for protection and automatic control of MV incoming distribution substation feeder . IED protect against different faults within protected zone (busbar) and performs back-up protection to all feeder protections in case of their failure. Automation functions include AR and automatic fault clearing & voltage restoration during some accidence within HV power lines. Terminal trips its incoming breaker after detecting under- voltage condition (black-out) on HV line and generates the close command to bus-coupler breaker for power restoration. After voltage restoration on HV line TOR 200 V IED opens bus-coupler breaker and closes its incoming breaker, following certain predefined rules.
Main functions
- PTOC/PIOC (50/51) - three-stage time delayed overcurrent protection
- PDEF/PSDE (67N) - two-stage time delayed directional earth fault overcurrent protection
- PPBR (46) - broken live conductor protection (unbalance protection)
- PVOC (51V) - voltage controlled overcurrent protection
- PTUV (27) - undervoltage protection
- PTOV (59) - residual voltage protection
- PDPR (32) - directional (power based) protection (for automatic fault clearing & voltage restoration)
- RBRF (50BF) - breaker failure protection
- RREC (79) - automatic reclosing
- CSWI - local and remote breaker control
- SCBR - circuit breaker status monitoring (control circuit, SF6 pressure, tripping time, etc.)
- RDRE - disturbance and event recording
- RFLO - fault location
- MMXU - measurements of current, voltage, frequency etc.
- local, warning and alarm signaling
- arc protection by sensor signal detection
- acceleration of current protection
- circuit breaker mechanical and switching life-time monitoring
- bus section voltage monitoring
- incoming line voltage monitoring
Incoming feeder protection for MV power plants incorporates additionally single step of distance protection.
Functionality of the IED can be changed according to certain technical requirements of customers.
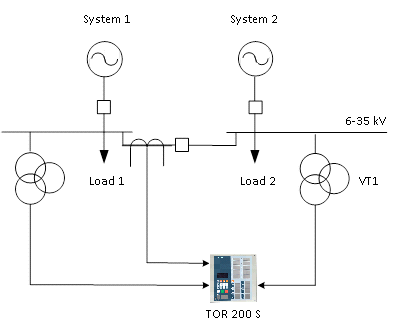
TOR 200 S devices are intended for protection and automatic control of MV bus-coupler breakers which perform bus-transfer automation (infeed transfer switching) and feeds the section busbars. IED fulfills this automation and protection functionality against different failures within bus-coupler powered section as an incoming feeder terminal.
Main functions
- PTOC/PIOC (50/51) - three-stage time delayed overcurrent protection
- PDEF/PSDE (67N) two-stage time delayed directional earth fault overcurrent protection
- PPBR (46) - broken live conductor protection (unbalance protection)
- PVOC (51V) – voltage controlled overcurrent protection
- PTUV (27) - undervoltage protection
- GAPC – infeed transfer switching
- RBRF (50BF) - breaker failure protection
- RREC (79) – automatic reclosing
- CSWI - local and remote breaker control
- SCBR - circuit breaker status monitoring (control circuit, SF6 pressure, tripping time, etc.)
- RDRE - disturbance and event recording
- RFLO - fault location
- MMXU – measurements of current, voltage, frequency etc.
- local, warning and alarm signaling
- arc protection by sensor signal detection
- acceleration of current protection
- circuit breaker mechanical and switching life-time monitoring
- bus sections voltage monitoring
- incoming line voltage control
Functionality of the IED can be changed according to certain technical requirements of customers.
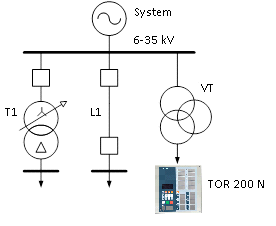
TOR 200 N devices are intended for monitoring and control of MV instrument voltage transformers and detecting of fuse failure events. IED measures three-phase und open-delta VY voltage. Break in the open-delta conductors are defined by the level of the third harmonic within open-delta voltage. Internal faults (short circuits) inside of VTs are protected by fuses. IED calculates phase voltages, negative- and zero- sequence voltages which are used for earth fault detection, operation of voltage-controlled protection functions and activation of the infeed transfer switching. Under-frequency and rate of change of frequency functions are used for the system load shedding automation. All these functionality defined the extremely high importance of reliable fuse failure functionality, provided by TOR 200 N terminals.
Main functions
- PTUV (27) - undervoltage protection
- PPBV (47) - negative sequence overvoltage protection
- PTOV /PVCB (60) - zero-sequence overvoltage protection
- PFRQ/PTUF (81) - under - frequency protection
- PFRQ/ PFRC (7) - rate of change of frequency protection
- RDRE - disturbance and event recording
- MMXU - measurements of voltage, frequency
- MHAI - monitoring of VT open- delta circuits integrity
- bus section voltage monitoring
Functionality of the IED can be changed taking into account certain technical specification of customers.
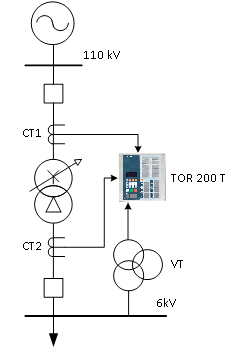
TOR 200 T devices are intended for relay protection and automatic control of step-down double-winding transformers up to 40 MVA. The IEDs are available in two functional modifications:
- transformer differential protection;
- transformer differential protection with back-up voltage-controlled protection.
Main functions
- PTDF (87T) - transformer current differential protection
- Buchholz protection of transformer
- Buchholz protection of tap changer tank
- PTOC/PIOC (50/51) - single-stage overcurrent protection on the LV side
- PTOC/PIOC (50/51) - broken live conductor protection
- PTOC (51N) - non-directional earth-fault overcurrent protection
- RBRF (50BF) - breaker failure protection
- PVOC (51V) - voltage controlled overcurrent protection
- RREC (79) - automatic reclosing
- CSWI - local and remote breaker control
- SCBR - circuit breaker status monitoring (control circuit, SF6 pressure, tripping time, etc.)
- RDRE - disturbance and event recording
- MMXU - measurements of currrent, voltage, frequency etc.
- current protection acceleration
Functionality of the IED can be changed according to certain technical requirements of customers.

High-speed automatic load transfer switching (ATS) terminal is intended to provide consumers with safe and continuous power supply providing under emergency conditions a high-speed automatic load transfer between MV busbar sections. It should be applied on distribution substations with independent highly sensitive MV loads.
High-speed ATS complex is based on TOR 300 HST device and high-speed vacuum circuit breakers.
Main functions
- identification of emergency conditions on busbars and on HV power supply line
- performing a sequences of switching operations resulting on incoming feeder changes
- control of synchronous closing of the bus-coupler breaker
- recovery function to normal conditions
- fault disturbance and event recording
 Main features
Main features
- 3-9 ms response time
- independent operation without connection to the existing PAC system
- reliable operation regardless of the type and composition of the load
- preventing emergency conditions for outgoing feeders and related loads
- reduction of the negative impact of production factors to employees’ health and working environment
- elimination of environmental disasters by prevention of hydraulic strikes in oil pipelines
- exclusion of commercial losses at industrial organizations caused by power supply interruption
- increasing service life of electrical devices
- ensuring optimal operating conditions for self-starting electrical motors after power supply restoration
- significant reduction of magnetic starters and contactors dropouts in 0.4 kV motors power supply circuits, computer-driven control system failures, disconnections of frequency and voltage converters
- operation under all types of short circuits including developing ones
- ability to realize the protections of main and bus-coupler breakers in high-speed ATS complex
The arc suppression coil (ASC), also known as Petersen coil, is used to compensate the capacitive earth fault currents supplied by substation outgoing feeders. With the centralized compensation design, one ASC unit will handle the compensation of all outgoing feeders. Ideal situation from the system point of view would be a 100% compensation degree, where the total capacitive earth fault current would be compensated. The centralized ASC must compensate the capacitive earth fault current supplied by a number of outgoing feeders. On the other hand, it is also noted that a compensation degree close to 100% would be preferred. To be able to fulfill these two conditions, it is clear that the inductive reactance of ASC has to be adjustable to match the different system-switching situations (feeder total length). The adjustment of the air gap will affect the coil’s inductance. The adjustment can be performed manually using a crank, or it can be automated (motorized). Such adjustment enables the use of a control device performing it automatically. The centralized ASC is connected between the system neutral point and earth, typically between the neutral of a star-connected main power transformer and earth. If the power transformer is delta-connected, the earlier introduced earthing transformer can be used to create the connection point.
We have developed a control device performing the adjustment of coil automatically. Excellent algorithm provides a close to 100% compensation degree.
Arc fault protection is a technique employed for the fast clearance of arcing faults on busbars and within metal clad switchgear and associated cable boxes. The arc is detected using optical sensors providing inputs to a protection device which also monitors the load current on the system. Conventional current based protection techniques are under arc conditions challenged by the nature of arching faults, and can result in slow protection initiated fault clearance times, which increase the risk to nearby personnel and the degree of damage to plant and equipment. By employing an optical detection technology, arc fault protection results in fast clearance of arcing faults.
Within an air insulated switchgear, the sensors are placed in such a way that arcs in the busbar, the circuit breaker and cable connection departments are reliably detected.
Relematika has an arc protection solution using optical sensors. Up to 4 optical sensors can be connected per arc protection unit. The sensors are powered and connected through a twisted-pair cable to the arc protection unit. The sensors detect arcs within their close environment and initiate protection in less than 1 ms. The arc protection unit trips the incoming and bus-coupler breakers taking into account short circuit currents. The arc protection unit has a built-in complete self-diagnostics. Different damages (breaks and short circuits) into the twisted pair cable are identified by self-diagnostics as well as loss of sensor sensitivity or its failure. The sensors have a built-in light-emitter which periodically lights and checks their sensitivity. They also prevent the blocking of arc protection due to dust or smoke influence, and reduce the life-time maintenance cost.